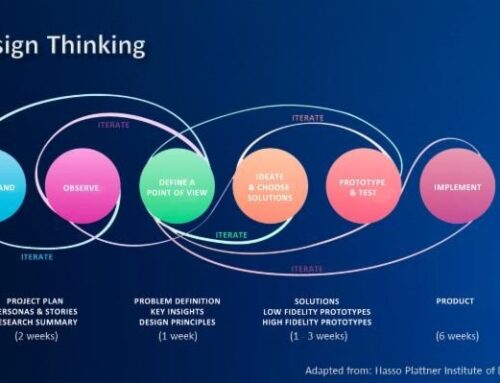
Introduction to Supply Chain Management
Supply chain management (SCM) is the wide range of functions that includes managing flow of raw materials from supplier to distribute, processing of the final product and then delivering to an end user in the most cost-efficient manner.
In SCM, not only movement of physical goods but also the flow of data or information, both inside and outside the enterprise should be focused.
SCM is the systematic approach to integrating and managing all functions related to producing a product. This approach includes sourcing and procuring products, production planning, material handling, inventory management, customer service, order processing, warehousing and transportation.
History of Supply Chain Management
In the early 60 plus ages of the history of supply chain management, fundamental base of improvement was built up the relatively simple but very human-work force processes. Now after 1990, primary focus of SCM has emerged to the applying modern engineering techniques into businesses and managing of very complex global networks with the help of specific strategies.
Six major movements in the evolution in SCM
- Creation Era
- Integration Era
- Globalization Era
- Specialization Era 1
- Specialization Era 2
- SCM 2.0
Creation Era
- In 1982,Keith Oliver introduced the term supply chain management.
- The supply chain in management had a greater impact long before, in the early 20th century, specifically with the creation of the assembly line. That means a manufacturing process in which parts complex parts should be fixed in the sequence with the semi-finished assembly until the final assembly is produced.
- The key feature of this era of supply chain management include the requirement for large-scale modifications, re-engineering, downsizing driven by cost reduction programs, and kindly focus upon the Japanese method of management.
Integration Era
- Main features of this era are increasing value added and cost devaluationusing integration.
- During the 1960selectronic data interchange (EDI) systems are developed and through the 1990s booster of supply chain management that is enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems are introduced.
- The development of this era is continued into the 21st century with the help of expanding Internet-based collaborative systems such as Slack, Microsoft Teams etc.
Globalization Era
In globalization era, global network of supplier relationships is extended,and supply chains are expanded beyond national boundaries and into other continents.
Specialization Era 1
- In this era, specific model develops manufacturing and distribution networks combined of several individual supply chain specific to producer to end consumer. Supply chain management introduces as a service-based industry.
Specialization Era 2
- There is a list of functions of Specialization Era 2 which can effectively prove that Supply chain management works as a service.Delivery Management, Storage and Inventory Management,Development Management and Performance Management.
SCM 2.0
- SCM 2.0 is a trend to explore the World Wide Web, that means to boost creativity, data sharing and collaboration among End users.
- According to the continuous increasing on-demand requirement of business, SCM 2.0 is devised to immediately deliver results with the rapid management of future changes for advancement of value and success of the business.
Latest Trends in Supply Chain Management
1. Evolving Technology
- Most of the emerging technologies like big data, predictive analytics, IoT, supply chain analytics, robotics and autonomous vehicles are also being used to solve modern challenges such as supply chain risk and sustainability.
IoT in Supply Chain Management
IoT enables businesses to do supply chain management better with the help ofasset tracking and fleet management.
- Asset Tracking: With the help of RFID tags or global SIMs asset tracking permits a supply chain manager to get the exact location of product, truck, or shipping container in real-time.
- Fleet Management: Best use of fleet management is generally got to see in FedEx or DHL drivers. Based on analysis, fleet management allows operators to know that package reliability, availability, and efficiency are all enhanced.
- Big companies such as Verizon and Cisco are also initiating in the area of global LTE network to encourage IoT services.Verizon has a Thing Space IoT management platform in which Cat-M1 chips are embedded. For designing and development of these chips Verizon collaborated with the Sequins. This step of support to IoT services would let enterprise users easily build and deploy devices suitable to urge their role in the supply chain process.
Block chain in Supply Chain Management
Block chain is digital, distributed transaction ledger that is spread over multiple systems owned by multiple entities having same data. Today block chain also stands as a gatekeeper in the emerging trust economy, in which supply chain plays an important role.
Supply chains are networks of independent companies that are integrated by informal agreements hence the trust is important factor in that chain. As block chain stands as a gatekeeper in the emerging trust economy,it will help to minimize the data inconsistency across business partners in a supply chain.
2. Future of Supply Chain Management
Robots
For years,the era of supply chain is rapidly changing due to autonomous mobile robots (AMR). During the growth of e-commerce and on-demand economy worldwide,autonomous mobile robots are becoming helping hand to companies to carry out a range of tasks in warehouses.
- AMRs can free labor workforce from day-to-day tasks and enable them to concentrate on more value-added activities.
- A wider enactment of AMRs by logistics companies across the world is expected in near future along with technological advances, maturity and reliability.
Drones
Drones finely works with inventory management, building inspections, yard management, intra logistics, and security.
While drone based package delivery is further out in the future, we can assume that the integration of drones into the supply chain may be here sooner than we think.
Conclusion
An efficient, flexible and aligned supply chains provide companies with sustainable competitive benefits.Supply chain management is nothing but provide the right items to the right customer at right time by most efficient manner. Supply chains support corporate strategies. Proper co-ordination between business strategies and supply chain tactics leads to the sustainable growth of business.